Launch Serial Port Tester
Once the settings are in order you can begin a new testing session by following these steps.
1. Launch Serial Port Tester
2. Choose “Session >>> New session” from the main menu. You can also use the keyboard shortcut “CTRL+N” or click “New” on the main toolbar.
3. The “New monitoring session” window will be displayed.
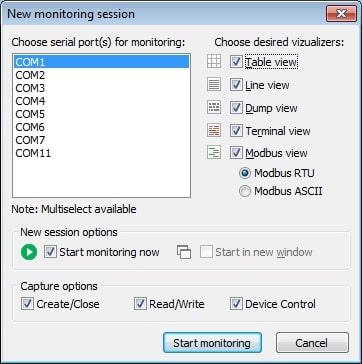
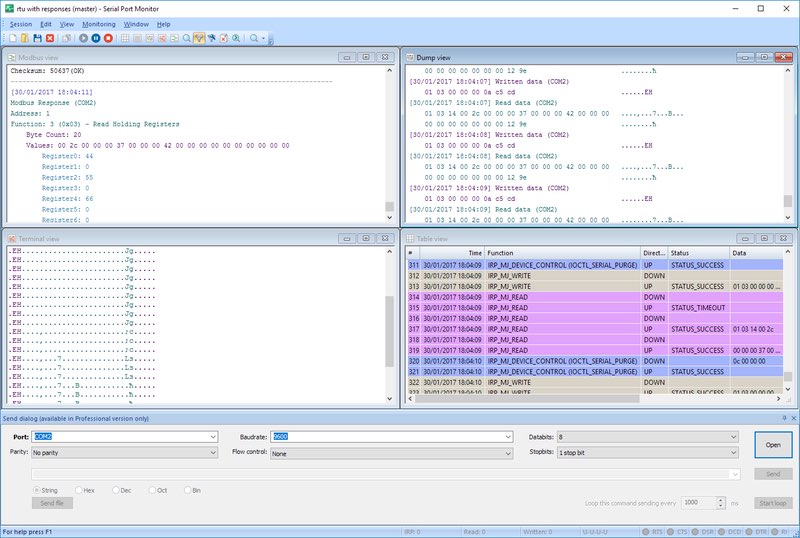
- Line view displays detailed information about the requests that are sent on a specific serial line.
- Table view presents the recorded IRPs in table format.
- Terminal view presents the received data in a text console of ASCII characters.
- Modbus view displays received and sent Modbus data (RTU and ASCII).
- Dump view displays all sent and received data transmitted through a serial line.
The checkboxes designated as “Start monitoring now” and “Start in new window” control how the new monitoring session is initiated.
Capture options: You can choose what you would like to monitor among these items - Read/Write, Create/Close, and Device Control.
Before monitoring, specify the COM port’s detail, which is connected to your computer. These parameters help you understand the data more closely.
nBaudRate: It indicates the baud rate of the serial port.
- Possible values for baud rate: These values could be anything from this list: 110, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 38400, 56000, 57600, 115200, 128000, 256000. 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200 are most common and well supported.
- Default baud rate: 110
nDataLength: It represents the number of data bits per data packet.
- Possible values for data length: 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- Default data length: 7
cParity: It indicates the parity or error checking method in a serial communication.
- Possible values for parity:
- • (E)ven
- • (O)dd
- • (M)ark
- • (S)pace
- • (N)one
- Default value: N (None)
nStopBits: It represents the number of stop bits located at the end of a dataframe.
- Possible values for stop bits: 1, 1.5, and 2
- Default value for stop bits: 1
cHandflow: It indicates the settings to control data flow (between a serial port device and a computer).
- Possible values:
- • P = Hardware (RTS/CTS lines)
- • X = Xon/Xoff (software flow control)
- • N = None (no flow control)
- Default value: N (None)
Note: Refer to your serial device’s documentation for all this information. IT will also help you understand how to check if COM port is working. Keep in mind the device settings should match Serial Port Monitor’s settings.
4. After you’ve set the options, click “Start monitoring” to initiate a new session.
5. You’ll see a new monitoring window with visualizers you’ve selected.
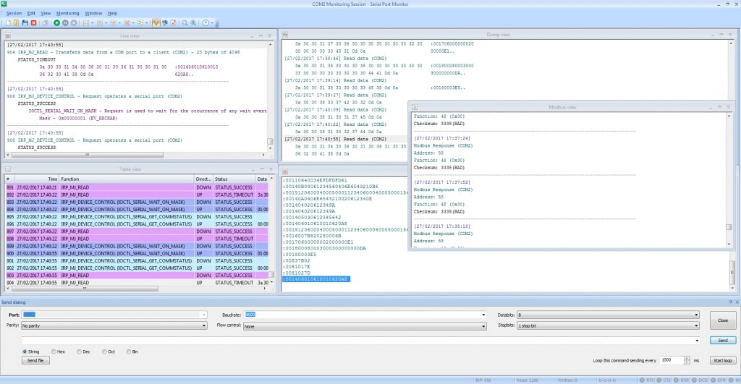
6. From the main menu, choose “Session >>> Save session/Save session As” to save a session.
Alternately, check the main toolbar to find “Save” and click it. Or, simply press CTRL+S keyboard shortcut to save the session.
7. If the system prompts, choose a file name for the session. This way, you can reload the session at a later time using this file and continue your work.
Once you’ve resolved issues in a serial port communication by following all the steps from 1 through 7, revert to step 1 again. This time, verify the status of the COM port lines.
COM Port Lines Status
Let’s understand what each status of the serial control lines actually means:
- RTS: Request to Send line indicator
- CTS: Clear to Send line indicator
- DSR: Data Send Ready line indicator
- DCD: Data Carrier Detect line indicator
- DTR: Data Terminal Ready line indicator
- RI: Ring line indicator
Based on color coding, here’s what each control line status translates to:
- Green: High level
- Red: Low level
- Gray: Inactive or unknown state
Advanced Troubleshooting
More complex issues may surface during a serial communication even after you’ve performed basic checks and corrected common serial port issues. As a result, the data you are expecting might not appear.
In this case, you need additional, advanced troubleshooting methods to detect the underlying issue. Let’s discuss these methods one by one:
Conduct a Loopback Test
In a loopback test, you’ll need to send data from a device and receive it back through the same COM port. This test verifies how the serial communication is working.
This test doesn’t require third-party hardware and checks:
- serial port
- cable connection
- software
The goal of a loopback test is to enable protocols, such as RS232, RS422, and RS485 to communicate properly:
- RS232: For this protocol, connect the TXD and RXD pins.
- RS422/RS485: For this protocol, connect TXD + to RXD + and TXD - to RXD -.
You will need to connect additional pins, such as CTS to RTS and DTR to DSR for advanced tests using hardware flow control.
How to Perform Loopback Testing with HyperTerminal
You can perform a loopback test using the HyperTerminal utility to simplify the process.
HyperTerminal converts your machine into a terminal. This offers you two advantages:
- Conduct communication tests over serial ports
- Connect to other systems
Let’s explore the step-by-step process to do a loopback test using HyperTerminal:
- Initiate a New Connection: Give this connection a name (e.g., “Loopback Test”). Now, choose an icon.
- Select the COM Port: After initiating the connection, choose the port for testing.
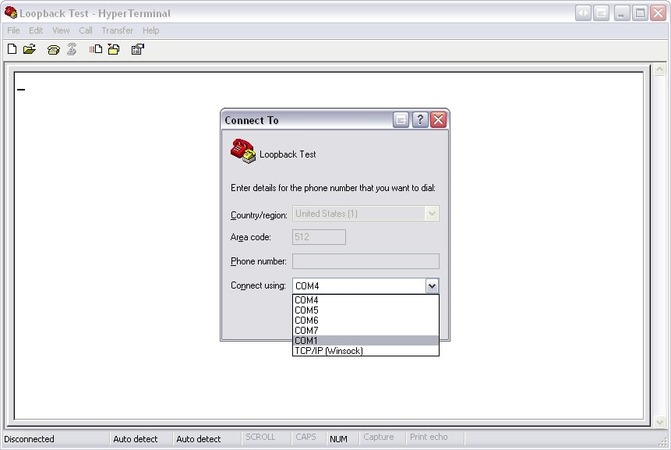
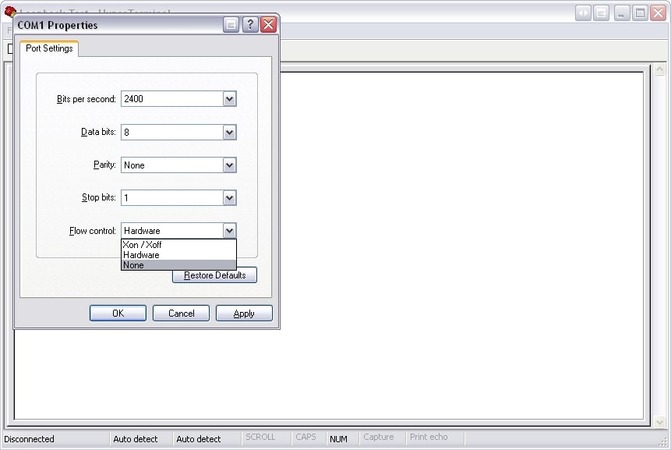
- Select flow control: Choose a flow control type: Xon/Xoff, Hardware, or None.
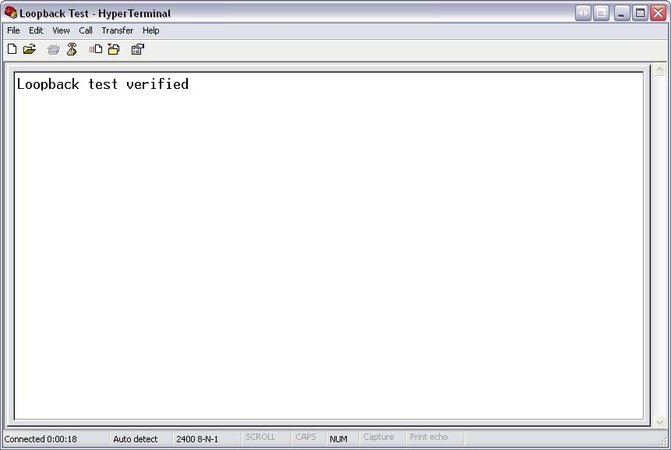
- Verify the test: Type a text message. Your loopback test is a success if the text reappears in HyperTerminal.
Enable Hardware Handshake
Set up a hardware handshake if your messages are not transmitting even after the signals are correctly wired.
Hardware handshaking assures that both sender and receiver devices are ready for data transmission, so you can control the data flow. Here’s how this works:
- A device can stop the data transfer if the other end is not ready to accept it.
- If a computer is not yet ready to receive data, it can stop the other device from sending data.
Note: Handshaking is not something you need to use often just because your computer supports this feature.
But if you need to use it, start by connecting handshake lines to fixed voltages. This prevents you from interfering with the operations running in the device. Also, there are resistors connected to handshake lines in many devices. So, you don’t need to tie them on your own.
In case you face these issues:
- Missed messages due to input buffer overflow
- The device is missing data because of receiving incomplete messages
Use Handshakes in Serial Port Tester
The Serial Port Tester software uses DTR/CTS handshaking.
- The DTR output indicates that the device is prepared to receive data
- The CTS input is used for data flow control.
The DTR should be kept high if no handshaking is needed. This helps connect unused inputs to your device.
If you want to disable handshaking:
- Connect CTS to RTS (pins 8 and 7)
- Connect DTR to DCD and DSR (pins 1, 4, and 6)
Do this setting on your device.
Enable Software Handshaking
A device sends an Xoff character to block data transmission if it’s unable to receive more data. And when the device becomes ready to accept data again, it sends the Xon character.
This is how Xon/Xoff handshaking works, and it’s a software-based data flow control.
If your device needs this type of handshaking, choose Xon/Xoff handshaking in the COM Port Tester.
Conclusion
It can be difficult to troubleshoot serial communication and test COM ports. But not if you follow the above instructions.
If you want to know how to check if COM port is working in a serial communication, start with preliminary checks. Gradually, use software, such as Serial Port Tester. If you still face issues in serial communication, resolve them with advanced methods, such as software and hardware handshaking and loopback tests.
Whether you’re facing issues due to handshaking protocols, port settings, or wiring, the above methods will guide you at each step. This way, your computer and the serial device can communicate and exchange data smoothly.