Many IT applications today utilize the RS232 serial communication protocol for data transmission. It is widely used in medical devices, professional A/V equipment, industrial automation, and various embedded systems. RS232 remains a relevant serial port protocol despite newer ones because it is simple and reliable.
However, RS232 is prone to several hardware and software issues. To resolve these problems, thorough troubleshooting of its connections is necessary. In this guide, we discuss basic diagnostic RS232 debug methods to help you identify and fix common COM port issues.
Hardware Troubleshooting: Diagnosing Common Physical RS232 Issues
If you suspect that the root of your RS232 troubles is hardware related, consider the following:
Perform Hardware Inspection:
Check if the physical connection is intact. Any faulty connection can hinder the effectiveness of software fixes.
Use the Right Cables
Use straight-trouble cables to connect DTE (computer) to DCE (modem). You may also use null-modem cables if you want to connect two DTE devices.
Look for Physical Damages
Search for possible cuts, kinks, or damages in the connectors. Even a single broken pin can terminate communication.
Understand the Function of Pinouts
TXD (for data transmission) connects to RXD (which receives data). Both devices must share GND (common ground).
Verify Flow Control
Check if the flow control lines, RTS/CTS or DTR/DSR, are wired correctly. This is to ensure that the systems utilize the hardware flow control efficiently.
Perform Voltage and Loopback Tests
To perform voltage testing, grab a voltmeter and confirm if the system uses the correct signal voltage. For the loopback test, connect TXD to RXD and send data. If the port receives the data back, it is working correctly.
Software Issues: Configuring Your Communication Correctly
Once you've confirmed that your hardware is in good shape, the next step is software configuration. Misconfigured software settings on the devices can disrupt even a perfectly wired connection. For software-related RS232 issues, an RS232 debug is invaluable.
Here’s how serial port debugging works.
Connect to the Correct COM Port
You must select the appropriate COM Port to perform serial debugging. To do this:
Step 1: Open Device Manager. Right-click the Start button > Proceed to the Device Manager > Expand 'Ports (COM & LPT).'
Step 2: Locate your device (e.g., USB-to-Serial Adapter) and note the COM port (e.g., COM3).
Step 3: Use the identified COM port in your debugging tool.
If you need to troubleshoot the COM port, you need to check if the device is properly connected. You might also need to update your system’s drivers. Another option is to utilize a suitable cable (RS232) with at least 3 wires for transmit, receive and ground. Some devices require extra wires for flow control (RTS/CTS or DTR/DSR).
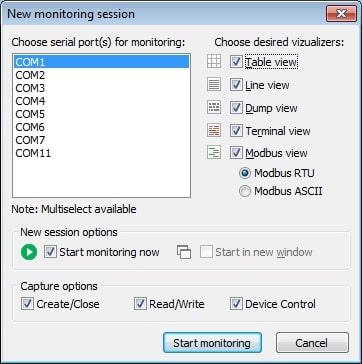
Configure Serial Communication Parameters
For a successful serial communication debugging, the parameters must be correctly set on both the device and software. Note that the values must be identical on both ends. Here are the recommended set up for various parameters
Baud rate: Data transmission speed (e.g., 9600 bps).
Parity: Error-checking type (e.g., none, even, odd).
Data bits: Number of bits per data packet (usually 8).
Stop bits: Marks the end of data packet (1 or 2).
Flow control: Manages data flow (e.g., RTS/CTS, XON/XOFF).
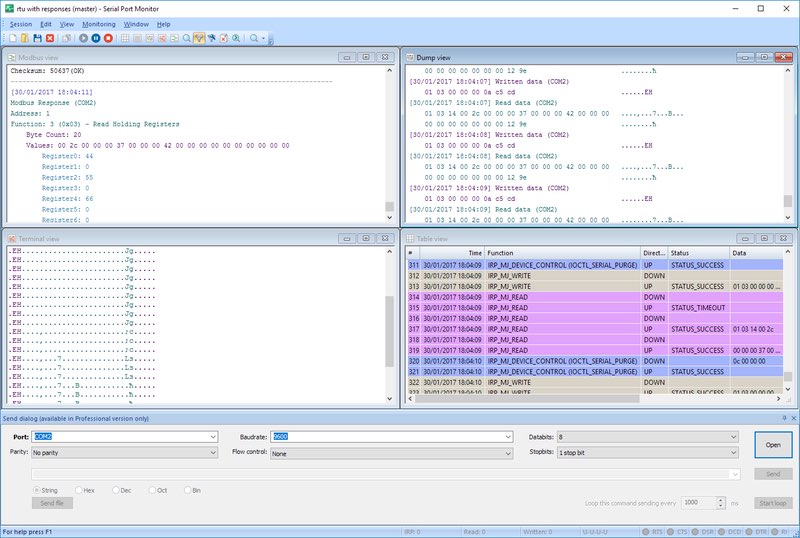
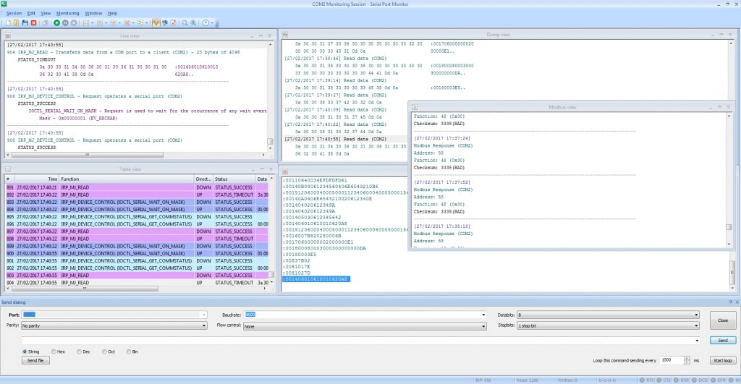
Use A Serial Port Debugger
A Serial Port Debugger is a software used for monitoring and analyzing the quality of serial port communication. This tool can capture and display transmitted and received data that can aid in the diagnostic of common serial port issues.